- Odds can be demonstrated by examining rolling a six-sided die. The odds of rolling a 6 is 1:5. This is because there is 1 event (rolling a 6) that produces the specified outcome of 'rolling a 6,' and 5 events that do not (rolling a 1,2,3,4 or 5). The odds of rolling either a 5 or 6 is 2:4.
- (2.40 x 2 = 4.80, 2.40 x 3 = 7.20, 2.40. 4 = 9.60, 2.40. 5 = 12) How to Work Out Implied Probability From Fractional Odds Divide the second number (denominator) by the total of the first number (numerator) and second number (denominator).
To calculate winnings on fractional odds, multiply your bet by the top number (numerator), then divide the result by the bottom (denominator). So a $10 bet at 5/2 odds is (10. 5) / 2, which equals $25. A $10 bet at 2/5 odds is (10. 2) / 5, which is $4.
If you want to come out on top against the bookies it is vital that you understand the fundamentals. When it comes to sports betting there is nothing quite as fundamental as the odds that the bookies offer. Unfortunately, betting odds can prove very confusing. That’s especially true for people who are new to betting.
That’s where this article comes in. We’re going to explain exactly how betting odds work, how they are set and the differences in the ways they are displayed. After taking in all the information below, you will be much better equipped to set about making some profit.
What Do Betting Odds Represent?
At their most basic, betting odds tell you two things:
- How much you stand to make should the selection win
- The probability of the selection winning
Take this example. If you were looking through the weekend Premier League fixtures and saw a team had fractional odds of 2/1 (that’s decimal odds of 3.0) you would know that you stand to win £2 in profit from every £1 that you stake should the team win. You’d also know that the bookmaker who set the odds ranks the team’s chances of winning as one in every three times the game is played.
If you saw a team had fractional odds of 8/13, you’d know that for every £13 you stake, you will win £8 or profit and that if the game was played 21 times in total, the bookies think the team would win 13 times and fail to win eight times (what is known as the implied probability).
Working out an implied probability percentage from fractional odds is simple. You just divide the stake by the combined sum of the two numbers which make up the fractional odds. In the case of 2/1 the equation looks like this:
1 / (2+1) = 0.33 or 33%
For odds of 8/13 this is the equation:
13 / (8+13) = 0.62 or 62%
That’s how the maths works but when it comes to the actual odds that bookmakers set, it’s a little more complicated.
How Do Bookmakers Set Their Odds?
The basic business model of a sportsbook is fairly uncomplicated. Bookmakers set the odds and take bets on an event. When that event ends they pay out everyone who backed the winner and then keep the rest for themselves.
But, consider the following horse race.
| Selection | Fractional Odds | Decimal Odds | Implied Probability | Profit From a £10 Bet |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horse 1 | Evens | 2.0 | 50% | £10 |
| Horse 2 | 3/1 | 4.0 | 25% | £30 |
| Horse 3 | 7/1 | 8.0 | 12.5% | £70 |
| Horse 4 | 7/1 | 8.0 | 12.5% | £70 |
As you can see, the combined implied probability of the selections above is 100%. From a bookmaker’s perspective that is a big problem. That’s because, presuming they’ve got the same amount of liability on each selection, they’d never make any money as they’d have to collect and payout the same amount.
So, the bookmakers will build something called an overround into their odds. Here’s a real example of a match odds market from a football match:
| Selection | Fractional Odds | Decimal Odds | Implied Probability | Profit From a £10 Bet |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Man Utd | 1/2 | 1.5 | 66.7% | £5 |
| Draw | 18/5 | 4.6 | 21.7% | £36 |
| West Ham | 13/2 | 7.5 | 13.3% | £65 |
With an total implied probability of 101.7%, the bookmaker who set those odds is guaranteed to make a profit of 1.7% assuming that they have the same amount of liability on all three selections. Of course, it rarely works out that the bookies manage to spread their liability evenly but you need to know that when you look at a betting market you’re not simply looking at a reflection of how the bookies think the event will pan out. There’s much more going on behind the scenes.
Armed with this knowledge of how the bookmakers set their odds, you can concentrate on finding value. That is, finding a bet where you believe the odds (and therefore the implied probability) is too big. If the bookies think that a side has a 50% chance of winning but you think they’ve got a better chance than that, that’s value.
The Difference Between Decimal and Fractional Odds
You will have seen above that we’ve spoken about both fractional and decimal odds. They are just different ways of conveying the same information but they do add another layer of complexity.
All the major online bookmakers will shows their odds as both fractions and decimals so it’s important that you understand just what they are showing and how to switch between the two. Thankfully, it only requires simple maths.
To go from a fraction to a decimal is as easy as dividing out the fraction and adding one. Here’s how that looks for odds of 2/1:
(2/1) + 1 = 3.o
And using our second example from above, 8/13, it looks like this:
(8/13) + 1 = 1.62
If you want to go from decimal odds to fractional odds is similarly simple. You just minus one from the decimal odds, turn that number into a fraction and reduce it down to it’s simplest form.
Let’s take decimal odds of 4.5, this is the equation:
4.5 – 1 = 3.5
35/10 -> 7/2
If the decimal price is 1.25, you convert it into fractional odds like this:
1.25 – 1 = 0.25
25/100 -> 1/4
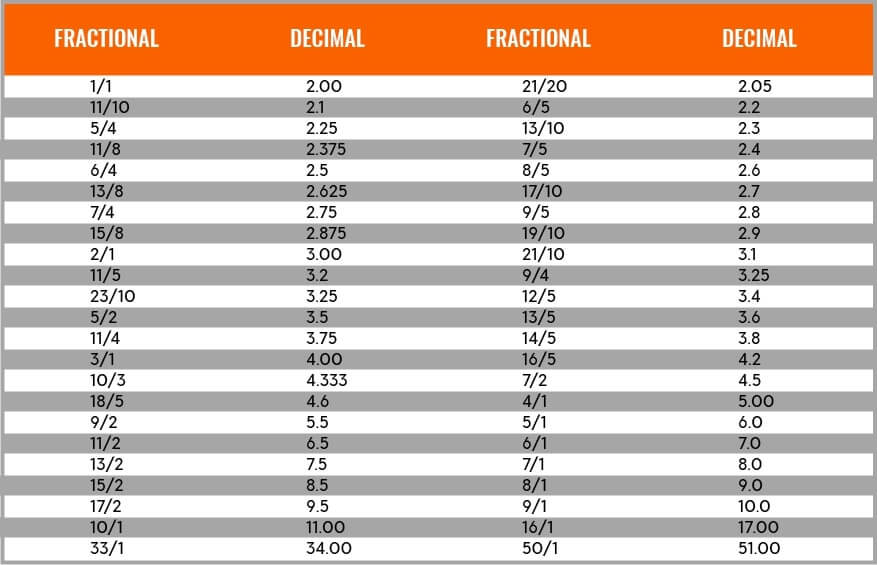
Here’s a list of some of the most common fractional odds and their decimal equivalents (for a more in-depth list click here).
| Fractional Odds | Decimal Odds | Implied Probability |
|---|---|---|
| 1/10 | 1.10 | 90.9% |
| 1/5 | 1.2 | 83.33% |
| 2/5 | 1.4 | 71.43% |
| 1/2 | 1.5 | 66.67% |
| 1/1 (evens) | 2.0 | 50% |
| 3/2 | 2.5 | 40% |
| 2/1 | 3.0 | 33.33% |
| 4/1 | 5.0 | 20% |
| 9/1 | 10.0 | 10% |
| 100/1 | 101.0 | 0.99% |
Key Terminology
When reading betting advice or searching for a value bet on the bookies’ websites you’ll come across some key terms relating to betting odds. To round up our article on betting odds, we’ve covered the most widely used terms to ensure you don’t get confused in your search for winners.
Stake – The amount of money that you place (or wager) on a specific bet.
Price – The price of a bet is simply another way of referring to the odds. You can either say that a football team can be backed at odds of 2/1or that their price is 2/1.
Odds On & Odds Against – Two of the key terms that you’ll hear when it comes to betting odds are ‘odds on’ and ‘odds against’. These terms refer to whether a price is greater or lower than evens. Any price above evens is known as odds against, while anything below evens is odds on.
Short and Long Odds – If something is described as being short odds it means the price is low. A long odds shot will provide you with a bigger win but is much less likely to win.
There are two ways odds – or prices – are displayed at racecourses in Britain: the traditional fractional system or the more recently introduced decimal system.
Fractional odds:

These are usually displayed in this format: 4/1.
In spoken form this is “Four-to-one” and sometimes this can be written as: 4-1.
Odds are just maths. To illustrate some examples, let’s call each number a unit. So:
4/1: For every 1 unit you stake, you will receive 4 units if you win (plus your stake).
7/2: For every 2 units you stake, you will receive 7 units if you win (plus your stake).
9/4: For every 4 units you stake, you will receive 9 units if you win (plus your stake).
If you see fractional odds the other way round – such as 1/4 – this is called odds-on and means the horse in question is a hot favourite to win the race.
In spoken form this is “Four-to-one on”.
1/4: For every 4 units you stake, you will receive 1 unit if you win (plus your stake).
1/2: For every 2 units you stake, you will receive 1 unit if you win (plus your stake).
Sometimes you will see Evens or EVS displayed. This is the equivalent of a 1/1 fraction. Again it means the horse in question is expected to win the race.
EVS: For every 1 unit you stake, you will receive 1 unit if you win (plus your stake).
Decimal odds:
These are usually displayed in this format: 5.00.
5.00: Simply multiply this number by your stake to calculate your total potential returns if you are placing a win bet. Unlike fractional odds, your stake is already factored into this price i.e. this is the equivalent of 4/1 plus the 1 unit you stake.

4/5 Odds In Decimal
Favourites:

Each race has a favourite. This is the horse most likely to win, which is reflected in having the shortest price displayed with betting operators.
You will see an F alongside the horse’s odds when they are the favourite. If more than one horse has the same odds of winning according to the betting market, this will be displayed as JF, meaning joint-favourite.
4/5 Odds In Decimal
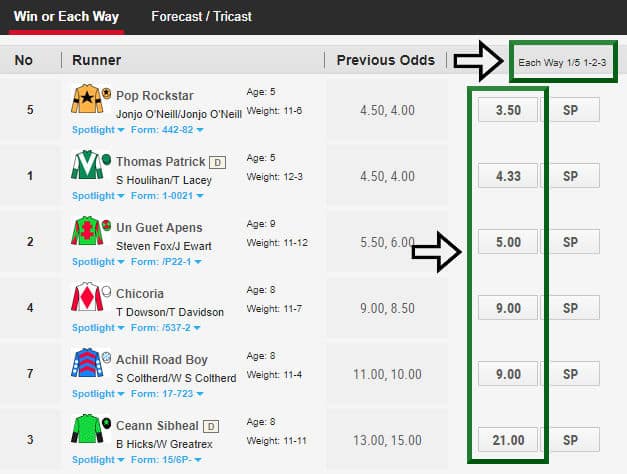
What about odds when betting each-way?
Racecourse bookmakers operating at Jockey Club Racecourses must meet (or exceed in the customer’s favour) a standard set of terms if you decide to place an each-way bet.
You will appreciate it is not affordable for bookmakers to pay out on all four places in a four runner race (!) so these agreed terms concerning place part of your each-way bet have to vary dependent on the number of runners and type of race. These are:
4/5 Odds Pay
• Races with 3 or runners: win bets only, unless the bookmaker chooses to offer 1/5 (one fifth) of the stated odds for finishing 1st or 2nd
• Races with 3 or 4 runners: 1/5 (one fifth) of the stated odds for finishing 1st or 2nd
• Races with 5 to 7 runners (inclusive): 1/4 (one quarter) odds for finishing 1st or 2nd
• Races with 8 or more runners: 1/5 odds for finishing 1st, 2nd or 3rd
• Handicap races with 12 to 15 runners (inclusive): 1/4 odds for finishing 1st, 2nd or 3rd
• Handicap races with 16 to 21 runners (inclusive): 1/5 odds for finishing 1st, 2nd, 3rd or 4th
• Handicap races with 22 or more runners: 1/4 odds for finishing 1st, 2nd, 3rd and 4th